The European Bureau of Report reports this with reference to the European Center for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC).
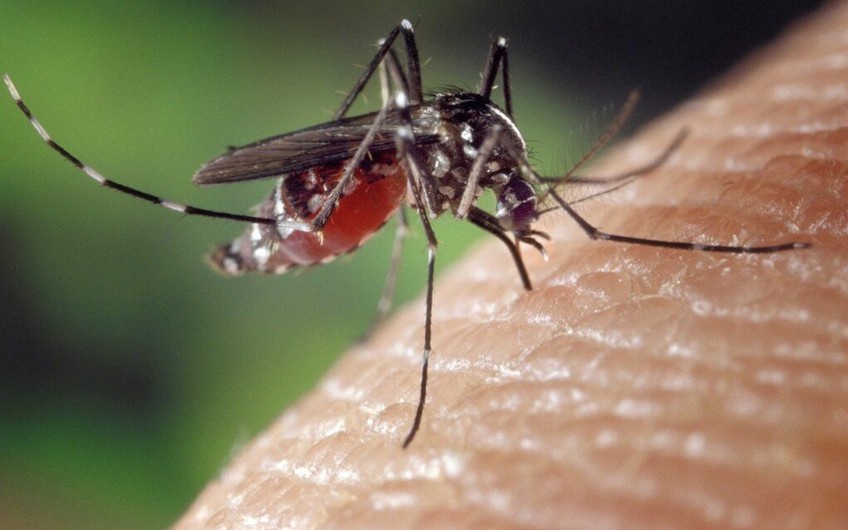
According to the agency, the continent has registered the maximum number of cases of chikungunya in the entire history of observations - 27, as well as 335 cases of West Nile virus - the highest number in the last three years.
"Europe is entering a new phase where longer–term, more widespread and more intensive transmission of mosquito–borne diseases is becoming the new normal," said Pamela Randy-Wagner, director of the ECDC.
The mosquito season on the continent is getting "longer and more intense" as temperatures rise, milder winters, and precipitation patterns change, creating ideal conditions for mosquitoes to breed and spread viruses, according to the ECDC.
Experts also warn that mosquito-borne diseases may become endemic in Europe as a result of climate change.
The distribution areas of these diseases are becoming wider.
According to the ECDC, the Asian tiger mosquito, the vector of chikungunya fever, is currently found in 16 European countries and 369 regions, compared with 114 ten years ago. And cases of West Nile virus infection are reported annually in new regions. In 2025, they were joined by the Salage county in Romania, the provinces of Latina and Frosinone in Italy, where at least 10 people died from the virus.