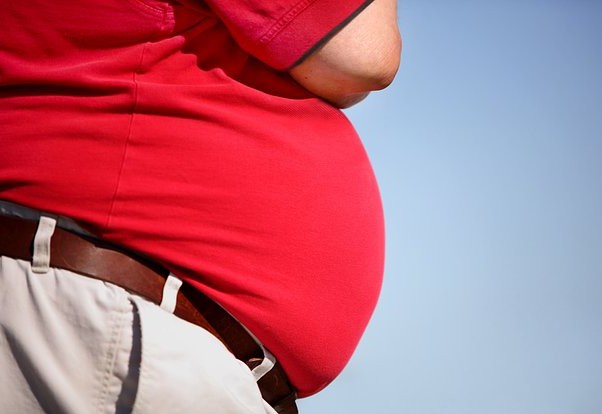
Specialists from Sechenov University (Russian Federation) have identified an ambiguous relationship between obesity and cancer. The greatest risk of cancer was found in people with obesity, which persists for more than 10 years, especially if it is combined with metabolic syndrome and poorly controlled metabolic disorders. About this "Lenta.ru was reported in the university's press service.
As observations have shown, it is not so much the excess weight itself that is of key importance, as its type. Genoid obesity (according to the "female" type) is not associated with high risks, whereas abdominal obesity — with the accumulation of fat in the abdominal area — is more often accompanied by cardiovascular, metabolic and oncological problems. An increased risk has also been identified in patients with sarcopenic obesity, when excess fat is combined with loss of muscle mass.
The researchers note that the likelihood of cancer increases dramatically if abdominal obesity lasts for more than 10 years and is combined with at least two components of the metabolic syndrome — for example, hypertension and disorders of carbohydrate or lipid metabolism. At the same time, patients who are overweight or obese of the first degree, but without treatment, get cancer more often than people with more severe obesity who regularly take medications and monitor their health indicators.
According to experts, successful treatment of diabetes, hypertension and other chronic conditions can reduce cancer risks. And patients with long-term abdominal obesity and lack of control over blood pressure, sugar and cholesterol levels should be considered as a priority group for in-depth medical monitoring. lenta.ru.