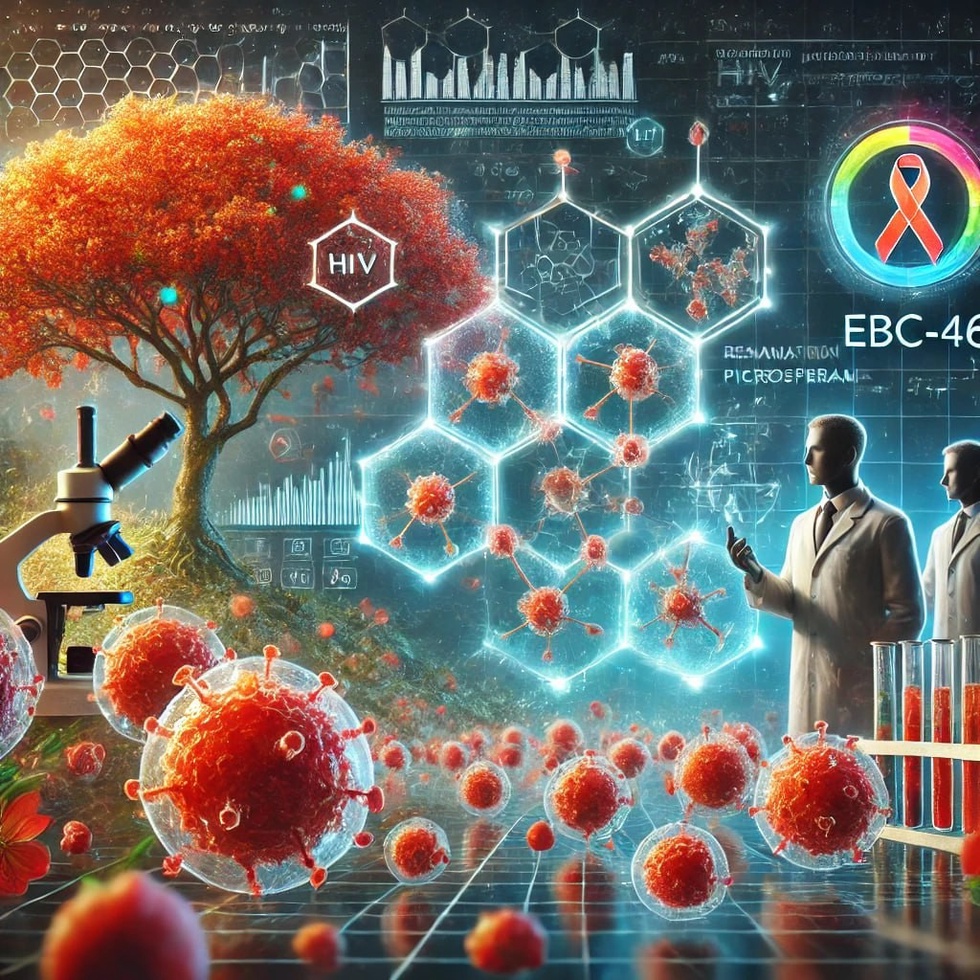
Stanford University scientists have discovered that the compound EBC-46, previously known for its anti-cancer properties, shows great potential in the fight against HIV.
EBC-46 activates dormant cells harboring HIV, making the virus vulnerable to immunotherapy. In the study, EBC-46 activated up to 90% of dormant cells, which is four times more effective than that of the most powerful previously known agent, bryostatin.
EBC-46 is naturally found in the fruits of the Fontainea picrosperma tree native to Australia.