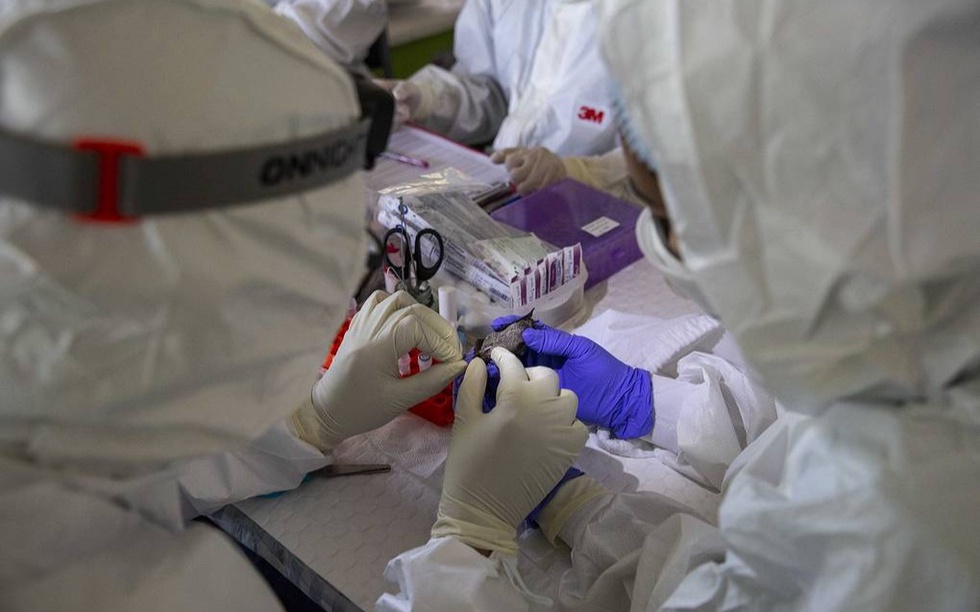
These pathogens can cause outbreaks of new zoonotic infections when bats come into contact with humans, the researchers write in an article in the scientific journal PLoS Pathogens.
"We analyzed a set of pathogens present in the kidneys of bats living in Yunnan Province near village orchards and in neighboring caves. During this analysis, we immediately identified two pathogens very close to the Hendra and Nipa viruses, whose penetration into populations of domestic animals or humans can lead to serious consequences," the researchers write.
The discovery was made by a group of Chinese molecular biologists led by Shi Man, a professor at Sun Yat-sen University, while studying a large number of bats caught in five regions of Yunnan Province between 2017 and 2021. In total, the researchers captured 142 bats belonging to ten species of bat-winged mammals common in southern China. tass.ru.